Glaucoma is an eye condition caused by increased Intraocular Pressure (IOP) that may lead to vision loss problems.
The serious eye condition commonly develops slowly and has no noticeable early symptoms.
Therefore, it is important to get regular eye checkups to help detect Glaucoma early.
Let us explore more about Glaucoma, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options to help you understand the condition better.
What is Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a category of eye conditions that may harm the optic nerve and cause vision problems.
The optic nerve is important for good vision as it sends visual information from the eye to the brain.
On the other hand, a damaged optic nerve may cause vision problems by breaking the communication of visual signals.
Therefore, Glaucoma can cause vision problems and these vision issues can often lead to blindness due to Glaucoma.
It is important to have regular eye checkups to detect Glaucoma early and for proper treatment.
Types of Glaucoma
The two primary types of Glaucoma are Open Angle Glaucoma and Closed Angle Glaucoma.
However, there are eight other types of Glaucoma that fall in the secondary category. These include Normal Tension Glaucoma, Congenital Glaucoma, and more.
Let us explore the different types of Glaucoma in detail.
Open-Angle Glaucoma
Open Angle Glaucoma is the most common type of Glaucoma that affects 9 out of 10 Americans.
It happens when your eye’s drainage tubes get blocked but look like they are open and working fine.
As a result, the eye fluid keeps increasing slowly and may damage the optic nerve.
The condition is also called the ‘silent thief of sight’ as it progresses slowly and does not have noticeable early-stage symptoms.
Closed-Angle Glaucoma
Closed Angle Glaucoma is less common but more serious.
It leads to a sudden increase in IOP by blocking or narrowing the eye’s drainage angle.
Closed Angle Glaucoma is also known as Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma or Narrow Angle Glaucoma.
Want to know more about the difference between primary Glaucoma types? Read: Open vs Closed Angle Glaucoma: An In-depth Comparison.
Secondary Glaucoma
Secondary Glaucoma occurs due to some underlying eye conditions like eye injury, surgery, or medications.
Most Secondary Glaucoma are different forms of the open-angle or closed-angle types.
The various types of Secondary Glaucoma are Normal Tension Glaucoma, Congenital Glaucoma, Traumatic Glaucoma, and more.
Glaucoma causes and risk factors
 Source: Rattankun_Thongbun_from_Getty_Images
Source: Rattankun_Thongbun_from_Getty_ImagesThe main cause of Glaucoma is high eye pressure (Intraocular Pressure).
Our eyes contain a clear fluid inside called aqueous humor which gets drained out of the eyes through a mesh tissue.
However, the blockage in the tissue may lead to high Intraocular Pressure (IOP) and harm the optic nerve.
Some less common causes of Glaucoma include eye injury, serious eye infection, or past eye surgery for some other eye condition.
One’s age can also be a major cause of high risk of Glaucoma.
Glaucoma is more common in older adults and is one of the main reasons for blindness in people over 60.
Some other risk factors may also contribute to the problem of Glaucoma. These risk factors include:
- A family history of Glaucoma
- Medical conditions like Glaucoma and Diabetes are connected.
- Thin Cornea
- Extreme near-sightedness (Myopia)
- Smoking
- Medicines like Corticosteroids (an anti-inflammatory medicine)
Glaucoma Symptoms
The symptoms of Glaucoma depend on the type and severity of your condition.
Open Angle Glaucoma has no early noticeable symptoms, but one may notice serious vision problems slowly.
As a result, advanced Open Angle Glaucoma may lead to tunnel vision and even blindness.
Tunnel vision: A visual problem in which the peripheral (side) vision is very limited, making the field of view narrow and tunnel-like.
On the other hand, one may notice more serious and sudden symptoms in the case of Closed Angle Glaucoma.
The symptoms of Closed Angle Glaucoma include:
- Eye pain or eye pressure
- Glaucoma headaches
- Halos around lights
- Low vision, blurred vision, tunnel vision, or blind spots
- Nausea and vomiting
- Glaucoma red eyes
Close Angle Glaucoma symptoms are very clear and cause quick damage.
In addition, the symptoms of Secondary Glaucoma are normally related to the underlying problem causing the Glaucoma.
Glaucoma tests and diagnosis
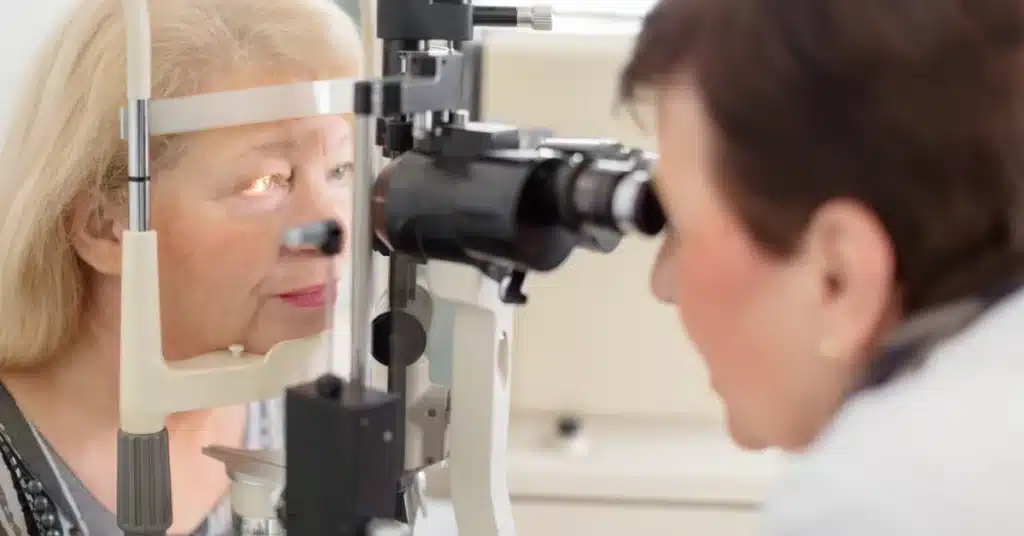
Consult a doctor for a proper Glaucoma test so as to prevent any chance of developing Glaucoma.
The doctor will discuss one’s condition after a comprehensive eye examination.
During an eye exam, your Ophthalmologist (eye doctor) will perform some tests to diagnose your eye health. These tests include:
- Tonometry: This test measures one’s Intraocular Pressure (IOP) and checks if the person has high IOP. The test is done using a device called a tonometer.
- Visual field test: The test checks your peripheral vision to detect problems.
- Ophthalmoscopy: This test checks the optic nerve health and looks for signs of damage.
- Gonioscopy: This test checks the drainage angle of your eye to determine the type of Glaucoma.
- Pachymetry: This test measures the cornea thickness.
Regular eye checkups are important since early-stage Open Angle Glaucoma does not have noticeable symptoms.
Also, Glaucoma is a progressive condition and may get worse with time.
Therefore, regular checkups are also important for monitoring changes in a patient’s condition.
Treatment of Glaucoma
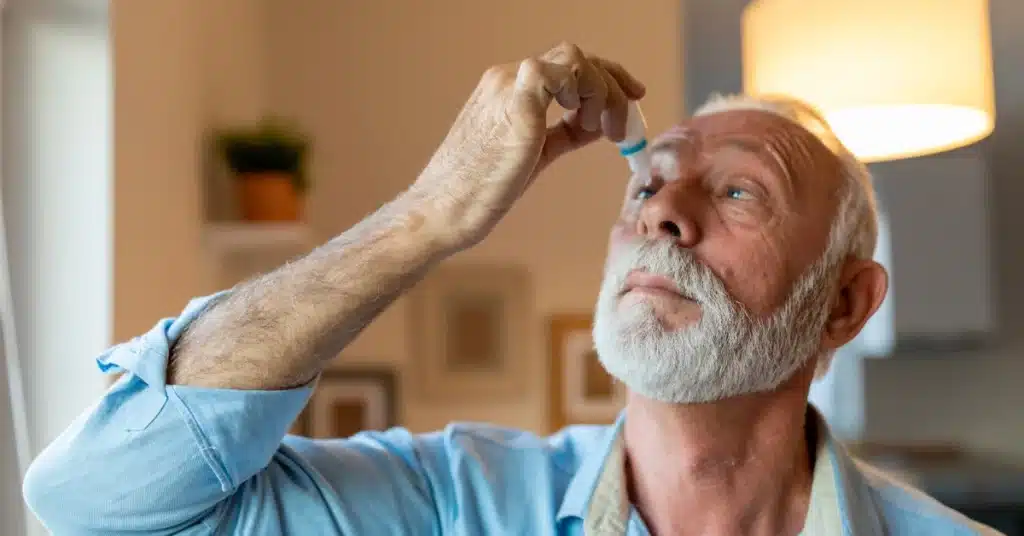 Source: RealPeopleGroup_from_Getty_Images
Source: RealPeopleGroup_from_Getty_ImagesThe Glaucoma treatment options include laser therapy, medications, and surgery.
While there is no cure for Glaucoma, the above treatment options may help manage the condition and slow its growth.
Let us discuss the treatment options in detail:
Medications: Medications for Glaucoma help the eye’s fluid drain better or stop the eye from making excess fluid. Glaucoma eye drops like Bimatoprost is an FDA-approved medicine to help manage Glaucoma.
Confused about which Glaucoma medicine to take and which not to? Read our article: Glaucoma Medications to Avoid: What You Need to Know
Laser therapy: The doctor may also recommend laser therapy along with Glaucoma medicines or when the medicines are ineffective. A study states that laser therapy is a safe and effective replacement of eyedrops for Glaucoma patients. Laser therapy like Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty and more can help improve fluid drainage from the eye.
Surgery: Doctors may recommend surgery when medications and laser treatments are ineffective. During the surgery, the doctor may implant a draining device to help lower the fluid pressure.
However, always consult a doctor before starting any Glaucoma treatment.
Your doctor can suggest a treatment plan depending on the type, causes, and severity of Glaucoma.
Glaucoma eye vs normal eye: A comparison
Many people are curious about how the Glaucoma eye is different from the normal eye.
Let us make the differences easier to understand by comparing them in a table.
Glaucoma eye vs Normal eye
| Basis of difference | Glaucoma eye | Normal Eye |
|---|---|---|
| Optic nerve health | Damaged optic nerve | Healthy optic nerve |
| Intraocular Pressure (IOP) | High | Normal |
| Vision problems | Tunnel vision, blindness, or other vision problems | Healthy vision |
| Risk factors | Age, genetics, ethnicity, medical conditions | No risk factors |
| Eye problems | May experience eye pain, red eye, or more | No eye problems |
People with Glaucoma may experience different Glaucoma symptoms and growth.
Therefore, it is important to get regular eye exams to help manage or prevent Glaucoma.
Curious about the vision loss pattern after Glaucoma looks like? Read: A Complete Guide on Glaucoma Vision Loss Pattern
Try Lashgrow 3 ml from GoodRxMedicine now.
Key takeaways
Glaucoma is an eye condition caused by high Intraocular Pressure that may lead to vision problems or even blindness.
High IOP can harm the optic nerve, which is important for visual information communication with the brain.
The symptoms of Glaucoma generally depend on the type and severity of Glaucoma.
However, common symptoms include cloudy vision, eye pain and redness more.
Fortunately, some treatment options like medicines, laser therapy, and surgery may help manage Glaucoma.
Be consistent with eye checkups and doctor appointments to get an early diagnosis and proper treatment plan for the problem.
Understand the difference between Glaucoma and Cataract with the help of our article: Understanding the Difference: Cataracts vs Glaucoma
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Glaucoma painful?
No, Glaucoma is not painful in most cases. However, Closed Angle Glaucoma can cause sudden eye pain and symptoms like headaches, nausea, and blurred vision.
Is Glaucoma Cancer?
No, Glaucoma is not Cancer. Glaucoma is a set of eye conditions that may cause vision loss problems. On the other hand, Cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
What does Glaucoma vision look like?
Glaucoma may not cause any vision changes in the early stages. However, advanced Glaucoma may lead to tunnel vision, a halo around lights, blurred vision, and even blindness.
Can I take marijuana for Glaucoma?
No, one should not take marijuana for Glaucoma. A study states that marijuana can reduce IOP for a few hours. However, its effects are short-lived and may cause unwanted side effects. Always talk to a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How to prevent Glaucoma?
One may prevent Glaucoma by adding some healthy lifestyle habits. These include avoiding smoking, managing Diabetes, reducing caffeine intake, and managing stress. Do regular eye checkups and use eye protection during risky activities.
When referencing outside resources, GoodrxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.











