Eyes are very complex and sensitive organs; even small substances can cause discomfort.
Eye pressure, formally known as Intraocular Pressure (IOP), is an important aspect of eye health.
Have you ever thought about what would happen if the pressure in your eyes changed?
This article will provide detailed information on eye pressure and the significance of high and low eye pressure.
We’ll also focus on how to measure eye pressure, its management, and the connection between eye pressure and Glaucoma.
What is Eye Pressure
Eye pressure, also known as Intraocular Pressure (IOP), measures the fluid inside the eyes.
This pressure is crucial for maintaining the shape of the eye and ensuring it functions effectively.
However, abnormal fluctuations, whether low or high eye pressure, can indicate underlying eye disorders.
Increased eye pressure can cause optic nerve damage and visual loss in conditions like Glaucoma.
As a result, regular eye examinations are recommended to identify changes in eye pressure.
Regular eye examinations and precise Intraocular Pressure (IOP) measurements are required to assess and maintain eye health.
Explore the link between Glaucoma and blindness with our article: Does Glaucoma Cause Blindness? Understanding the Risk and Prevention
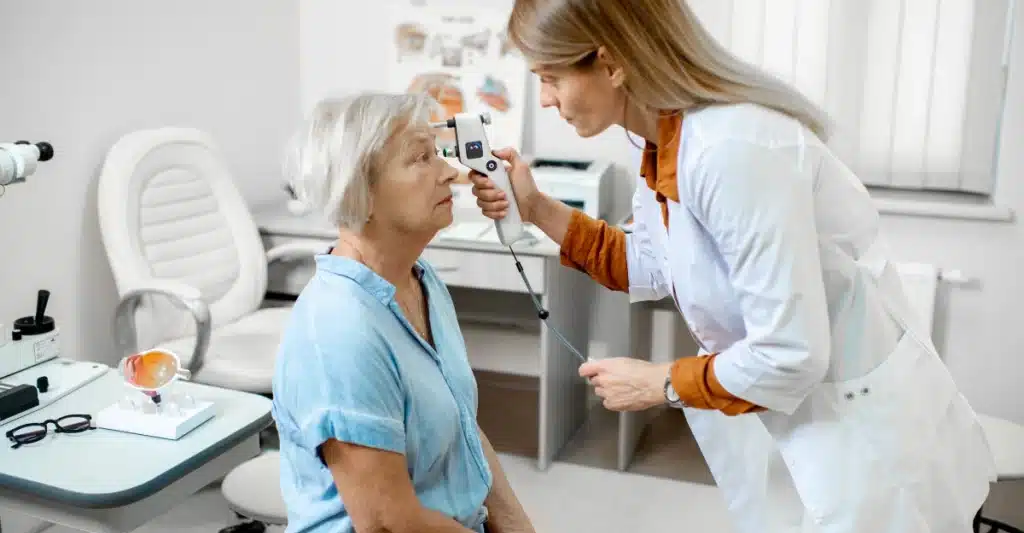
How to measure Eye Pressure
A licensed ophthalmologist can help you measure the pressure in your eyes.
Tonometry is a test that eye doctors can use to measure the pressure in your eye.
A tonometer measures the Intraocular Pressure by flattening the cornea in our eyes.
The higher the pressure in the eye, the greater the force required to flatten the cornea.
Visit an eye specialist regularly to have your eye pressure professionally measured.
Do you have doubts regarding the eye pressure test? Read our article Eye Pressure Test to clear all your doubts regarding eye pressure.
Normal Eye Pressure range
Age and overall health might have an impact on eye pressure. However, it should not reach levels that could harm your eyes.
Normal eye pressure ranges between 10 and 20 mmHg.
This range allows for supporting the eye’s internal structures without causing harm.
It is important to remember that this pressure is not constant and might vary between individuals.
Deviation from this normal range, whether excessively high or too low, can indicate potential eye issues.
Such deviations may require medical attention to ensure the preservation of eye health.
To know more about eye pressure range, read our article: Eye Pressure Range
High Eye Pressure
High eye pressure occurs when the pressure within the eyes exceeds the usual range.
It is also known as Ocular Hypertension, where the Eye Pressure Range exceeds 21mmHg.
Ocular Hypertension, unlike any other eye medical disease, has no symptoms.
However, some individuals may notice symptoms like blurred vision, headache due to high eye pressure, eye pain, and red eyes.
Common risk factors for high eye pressure include family history, age, ethnicity, and eye injury.
High eye pressure is also the most common Glaucoma cause, a vision-threatening eye disorder.
Regular eye checkups are important for early detection of high eye pressure to avoid potential risks.
Explore the connection between stress and eye pressure. Read our article: Can Stress Cause High Eye Pressure for effective eye health.
Low Eye Pressure
 Source: RossHelen
Source: RossHelenLow eye pressure, or Hypotony, is when the pressure inside the eye falls below the normal range.
While it’s not as common as high eye pressure, it may lead to visual disturbances.
It causes the eye pressure to fall below the usual range, i.e., below 10mmHg.
Some of the symptoms of low eye pressure are sensitivity to light, redness, and changes in vision.
Eye specialists can help in the safe and effective management of these symptoms to avoid low eye pressure.
If you notice symptoms of low ocular pressure, you should seek emergency medical assistance.
Suffering from high eye pressure? Read How to Lower Eye Pressure to make an informed decision regarding effective solutions for high eye pressure.
Link between Eye Pressure and Glaucoma
Understanding the link between eye pressure and Glaucoma is crucial for eye health.
Increased Intraocular Pressure is a major risk for developing Glaucoma symptoms.
This increased pressure in the eyes can damage the optic nerve, impairing vision or even blindness.
The amount of pressure the optic nerve can endure determines the risk of developing Glaucoma.
Not all individuals with high eye pressure develop Glaucoma.
Some individuals with normal eye pressure may still develop the condition.
Glaucoma can be hereditary; conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and Diabetes may higher Glaucoma risk.
Damages from Glaucoma including visual loss, may be avoided if Glaucoma treatment is received on time.
Glaucoma eye drops like Careprost may help control Glaucoma symptoms by lowering IOP.
Discover the truth about Careprost safety Read our article: Is Careprost Safe? Understanding the Risks and Benefits to make informed decisions.
How to manage Eye Pressure
Eye pressure can be managed using various methods, including medical treatments, vitamins, supplements, and food.
For optimal management, it is essential to consult with a licensed ophthalmologist.
Medications, lifestyle changes, and supplements are measures to manage eye pressure.
Let’s discuss these measures in detail:
Medical treatments
Several treatments may be available to help in managing fluctuations in eye pressure.
Eye drops are the most widely prescribed treatment for high eye pressure.
Bimatoprost and Latanoprost eye drops may help lower eye pressure and prevent eye injury.
In addition to these eye drops, oral medicines, and laser therapy may help relieve eye pressure.
Eye drops are the most effective therapeutic choice for managing eye pressure.
In severe situations, however, medication and laser therapy may be useless.
In such cases, doctors may advise getting surgery to manage eye pressure.
Discover the various eye pressure eye drops available with our article: Eye Drops for Eye Pressure: An Effective Way to Improve Your Vision
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes are vital in managing eye pressure and safeguarding your vision.
Poor lifestyle choices might not directly affect eye pressure but may increase individuals’ stress levels.
Stress is a known risk factor for increasing eye pressure. Stress reduction may help in the management of elevated IOP.
As a result, reducing stress levels through lifestyle changes may minimize the chances of high eye pressure.
Regular exercise and stress management are primary healthy lifestyle practices.
A balanced diet and limiting the intake of alcohol and caffeine consumption are additional ways to help in the control of eye pressure.
Increase your understanding of foods which help in reducing eye pressure, Read Foods to Reduce Eye Pressure
Supplements for eye pressure
 Source: LumenSt from Getty Images
Source: LumenSt from Getty ImagesAside from medical treatments, a variety of vitamins might help in the management of eye pressure.
Vitamins A, C, D, and E may help lower high Intraocular Pressure.
Leafy vegetables like spinach and kale and seafood such as salmon and mackerel are also believed to reduce eye pressure.
However, unlike medical treatments, these foods and supplements have inadequate studies on their use for lowering eye pressure.
As a result, it is important to visit an eye specialist to appropriately manage eye pressure.
Managing eye pressure is crucial for maintaining eye health, particularly in preventing conditions like Glaucoma.
Get to know about the various vitamins that can help reduce eye pressure with our article: Vitamins to Reduce Eye Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide
Summing up
Eye pressure is a measurement of the amount of fluid in the eye. It is also referred to as Intraocular Pressure (IOP).
Individuals have a different range of eye pressure. The usual range of eye pressure, however, is 10-21mmHg.
Understanding and regulating eye pressure is vital for preserving clear vision.
Increased eye pressure may increase the risk of Glaucoma.
However, individuals with high eye pressure don’t need to acquire Glaucoma.
Low eye pressure, although less common than high eye pressure, can have significant implications for eye health and vision.
Regular eye checkup is necessary for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Eye drops, oral medications, laser therapy, and surgery may help regulate the fluctuation in eye pressure.
Aside from these medical therapies, vitamins and lifestyle changes may also assist in restoring normal eye pressure.
As a result, regular eye examinations are recommended to identify changes in eye pressure before they create any problems.
Understand what pressure behind the eyes means with our article: Pressure Behind the Eye and its Potential Risk Factors
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check my Eye Pressure at home?
Checking eye pressure at home is not recommended. Accurate measurement requires specialized equipment and training.
Regular eye exams with an eye specialist are the best way to monitor eye pressure.
What is considered a normal range for Eye Pressure?
Normal ocular pressure is between 10-20 mmHg.
If your eye pressure is less than 10 mmHg or greater than 20 mmHg, seeking immediate eye care is essential.
An authorized eye expert can promptly evaluate to prevent potential eye injury.
What are the symptoms of High Eye Pressure?
Symptoms of high eye pressure may include blurred vision, eye pain, headaches, and the appearance of halos around lights.
However, it often progresses silently without noticeable symptoms, making regular eye exams crucial.
Do steroid eye drops raise blood pressure?
Steroid eye drops, when absorbed systemically, can potentially raise blood pressure.
It’s essential for individuals using these drops to monitor blood pressure and consult with a healthcare provider to manage any potential effects.
What causes Low Eye Pressure?
Various factors might cause low eye pressure, also known as Ocular Hypotony.
Low Eye pressure can be caused by various circumstances, including eye surgery damage, medications, ocular inflammation, and fluid leaking.
Ocular Hypotony should be treated at a reputable ophthalmology facility.
When referencing outside resources, GoodRxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.











