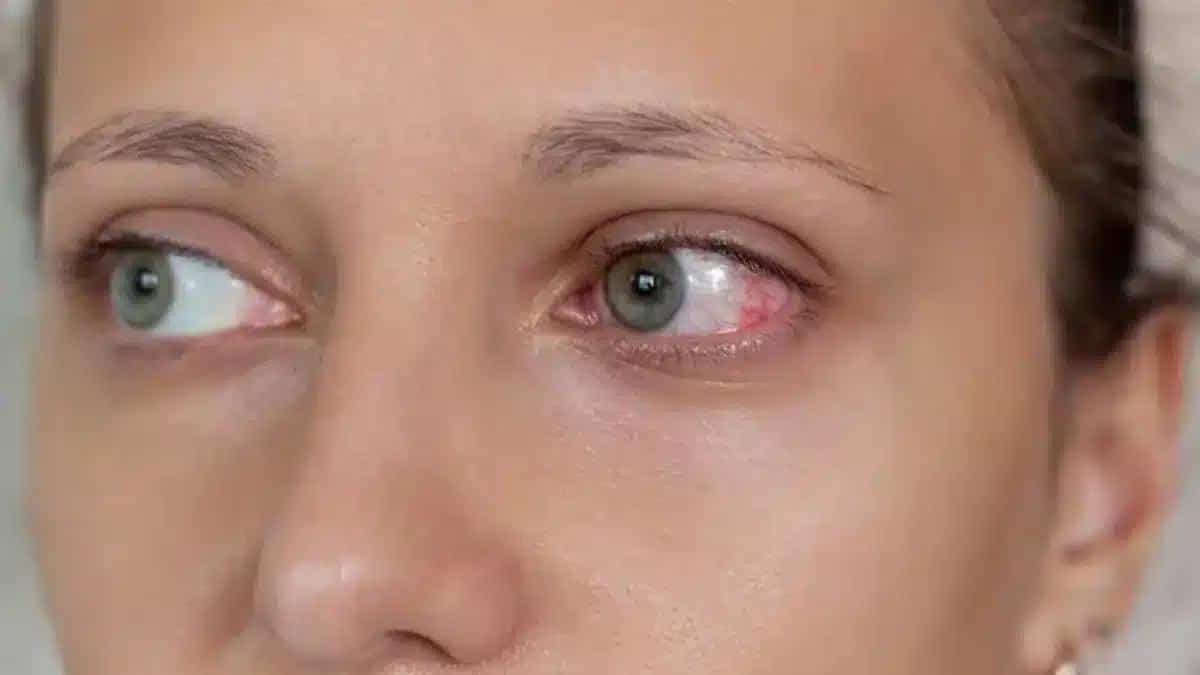
Uveitis is a serious eye condition that causes swelling in the uvea, the middle layer of the eye.
This condition can be painful, and the eyes may become red and clouded.
A viral or bacterial infection, an eye injury or other underlying conditions can cause Uveitis.
If left untreated, Uveitis can cause vision loss; thus, seeking medical attention and proper treatment is critical.
This article explores Uveitis, its symptoms, causes, types, treatments, and medications available.
What is Uveitis
Uveitis is an inflammatory disorder that affects the transparent middle layer of the eye, the uvea.
The uvea is made up of the iris (the coloured area of the eye), the ciliary body (which aids in lens focusing), and the choroid (which connects the retina to the sclera).
This condition can affect people of all ages and may be caused by autoimmune disorders, infections, or underlying conditions.
Uveitis is an eye disorder that distinguishes itself from other eye infections such as Pink Eye and keratitis.
Although Uveitis can be treated, the condition can sometimes become chronic and necessitate long-term care.
Read: How Long Does Blurred Vision Last with Uveitis? to understand the connection between Uveitis and blurred vision.
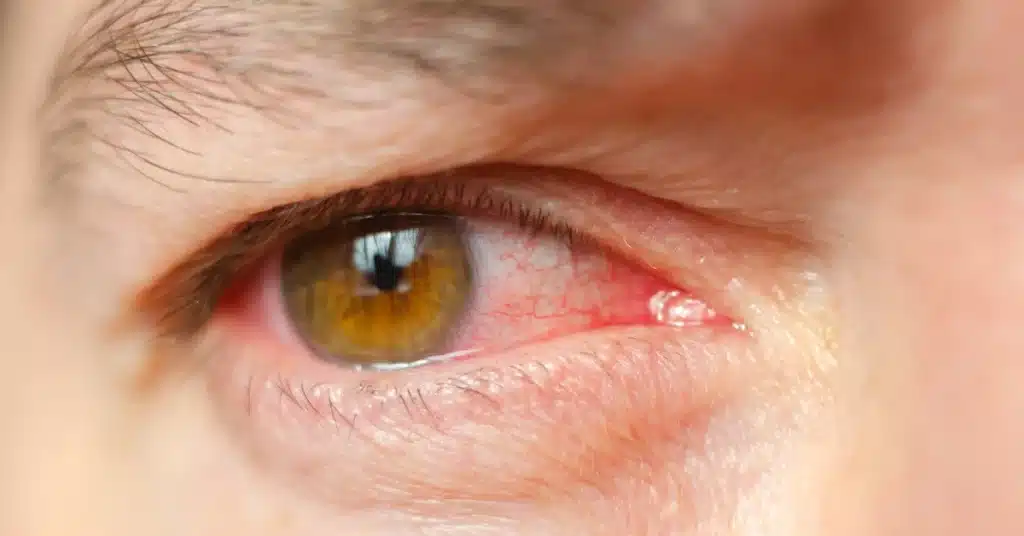
Types of Uveitis
 Source: Andrei310_from_Getty_Images
Source: Andrei310_from_Getty_ImagesUveitis is broadly classified into Anterior Uveitis, Intermediate, Posterior, and PanUveitis.
It is categorized into different types of Uveitis based on the specific site of inflammation within the eye.
Let’s discuss these types of Uveitis in detail:
Anterior Uveitis
Anterior Uveitis, often known as Iritis, is the most common type of Uveitis.
It refers to inflammation of the iris and the front portion of the uvea.
The symptoms of Anterior Uveitis may include redness, sensitivity to light, and pain.
It is important to seek medical assistance if you experience symptoms of Anterior Uveitis to avoid potential risks.
Read Anterior Uveitis: What You Need to Know to learn more about Anterior Uveitis.
Intermediate Uveitis
Intermediate Uveitis is a condition that affects the choroid and may spread to the retina.
Blurry vision and eye pain are symptoms of this eye condition.
Symptoms of Intermediate Uveitis may persist for a few weeks or many years.
The duration of the symptoms may vary depending on whether a person’s condition is improving or deteriorating.
Posterior Uveitis
The retina and choroid are inflamed in Posterior Uveitis. The back of the eye is referred to as Posterior.
Unlike other types of Uveitis, this is frequently severe and can endanger one’s vision.
Blurred vision and even loss of peripheral vision are some additional symptoms of Posterior Uveitis.
Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid serious complications and potential vision loss.
Don’t let Posterior Uveitis go unnoticed. Read Posterior Uveitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options to uncover the facts about the condition.
PanUveitis
PanUveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects all layers of the uvea.
Other parts of the eye, such as the lens, retina, optic nerve, and vitreous, might be affected by this type of Uveitis.
It can cause visual loss and blindness if left untreated.
To know more about Uveitis variations, Read Different Types of Uveitis:Their Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options and make informed choices for your eye health.
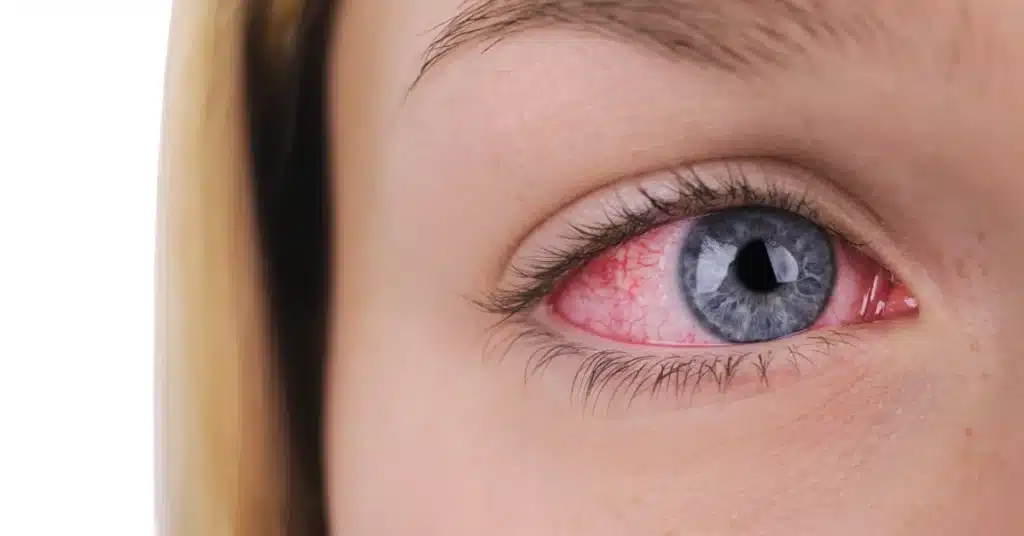
Symptoms of Uveitis
 Source: Alajsdfas
Source: AlajsdfasUveitis symptoms differ among individuals, depending on the affected part of the uvea.
They often occur suddenly, but can also appear gradually.
Among the possible symptoms are:
- Redness
- Eye pain
- Blurry vision
- Floaters
You should see your eye doctor if you have any of the mentioned symptoms.
Uveitis can cause vision loss if not treated; thus, regular checkups and medical attention are required.
Are you experiencing Uveitis? Read Managing Uveitis Symptoms:Identifying and Addressing the Symptom to learn about the symptoms of Uveitis and stay informed.
What causes Uveitis
Uveitis has numerous causes, which can range from infections to autoimmune conditions.
Some causes of Uveitis are eye injury, a viral or bacterial infection, or other underlying illnesses.
It might occur as a result of eye damage and the use of certain medications like Rifabutin.
According to one study, Infectious Uveitis is one of the most common and risky causes of Uveitis in the US.
Trauma, infections and autoimmune diseases frequently cause severe eye inflammation.
Some of the causes of Infectious Uveitis are:
Bacteria: Streptococcus and Staphylococcus Aureus
Virus: Herpes Simplex and Cytomegalovirus and Rubella virus
Parasites: Toxoplasma Gondii
Some of the autoimmune factors of Uveitis are:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
Eye injury which can cause trauma or chemical exposure may also lead to Uveitis.
Medications such as Cidofovir, Cobalt, Diethylcarbamazine, and Pamidronic acid can cause drug-related Uveitis.
Discover the triggers behind Uveitis; Read Exploring Uveitis Causes: From Infections to Autoimmune Factors for valuable insights for better eye care.
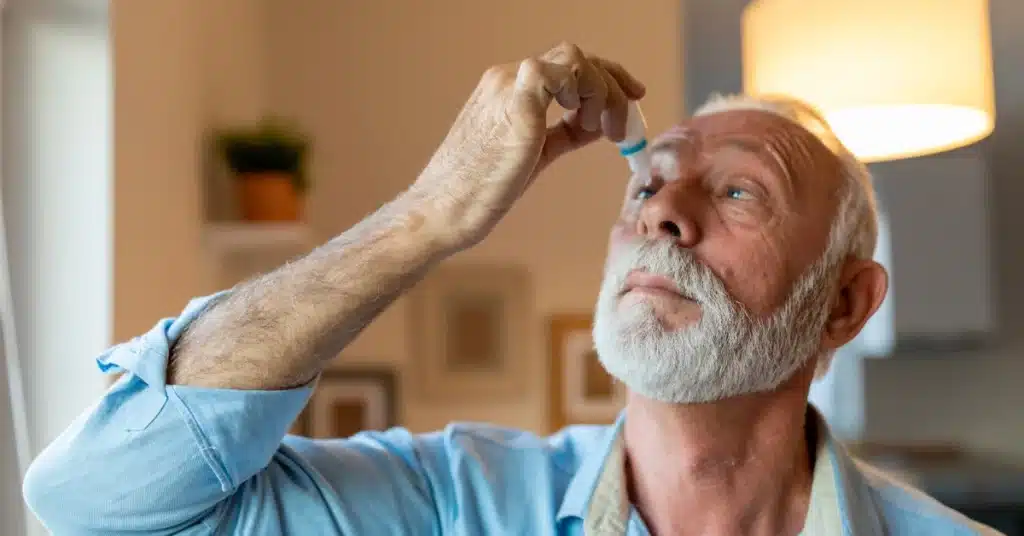
Available Uveitis treatment
 Source: RealPeopleGroup_from_Getty_Images
Source: RealPeopleGroup_from_Getty_ImagesIndividuals with Uveitis who receive quick and appropriate treatment frequently recover.
The most common treatment for Uveitis is corticosteroid drops, which help reduce inflammation.
Depending on the severity of your problem, your doctor may recommend surgery to treat Uveitis.
Vitrectomy and retinal treatment are common surgical procedures used to treat non-infectious Uveitis.
Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising daily, and regular eye checkups may also help with Uveitis.
Let’s discuss medications available for Uveitis and foods to avoid with Uveitis:
Discover the best Uveitis treatment for you! Read Uveitis Treatment: What You Need to Know and uncover a range of treatment options.
Uveitis medications
Steroid eye drops such as Prednisolone are administered to relieve swelling and pain.
Antivirals and antibiotic eye drops are effective in the treatment of infectious Uveitis.
Immunosuppressive medications, such as Methotrexate or Azathioprine, could also regulate the immunological response.
These medications reduce inflammation and avoid issues for individuals with Uveitis.
To learn more about Uveitis medications in detail, Read What is the Best Uveitis Medication: Your Path to Recovery
Foods to avoid with Uveitis
Uveitis management involves not only medication but also dietary concerns.
Certain foods can increase inflammation in the body, hence impacting Uveitis.
Avoiding intake of sugar and processed foods may help in increasing inflammation.
Saturated fat-rich foods like red meat and dairy can worsen inflammation.
Individuals can alleviate symptoms by eating a diet high in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and Vitamin A.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice.
A comparative analysis between Uveitis and other eye conditions
Uveitis is different from several other eye-related medical conditions.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Here’s a table for a better understanding of these eye conditions:
| Characteristics | Uveitis | Glaucoma | Iritis | Scleritis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light | Vision loss, halos around light | Redness, eye pain | Severe eye pain, redness |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease, infections, eye trauma | Increased eye pressure due to fluid buildup | Autoimmune diseases, infections | Autoimmune diseases, infections |
| Treatment | Steroid eye drops, oral medications | Eye drops, surgery | Eye drops, immunosuppressants | Steroids, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Complications | Vision loss, Cataract, Glaucoma | Vision loss, optic nerve damage | Vision impairment, structural eye damage | Vision loss, Cataracts, synechiae (adhesions) of iris |
Each of these conditions has its particular treatment; therefore, consulting a doctor is critical to get an accurate diagnosis.
Learn more about the difference between the common eye conditions, Read Keratitis vs Uveitis: Clearing the Confusion and clear the confusion.
Summing up
Uveitis is a serious eye condition that causes inflammation in the middle layer of the eye.
There are four types of Uveitis namely, Anterior, intermediate, Posterior, and PanUveitis Uveitis.
Some of the symptoms of Uveitis are redness, eye pain, and blurry vision.
Infections, autoimmune conditions, trauma, and drug-related issues are all possible causes of Uveitis.
Doctors typically recommend antivirals, antibiotics, steroids, and immunosuppressive medications for treatment.
Antibiotics, antivirals, and steroid eye drops like Prednisolone may help treat Uveitis.
It is essential to avoid foods such as processed foods, saturated fats, and more along with medications to properly manage Uveitis.
It is best to seek medical advice for early diagnosis and proper treatment to avoid any potential risks and side effects.
Wondering about the difference between Uveitis and Conjunctivitis, Read Uveitis vs Conjunctivitis: Understanding the Key Difference and understand the conditions in detail.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of Uveitis?
Infections, autoimmune disorders, trauma, or idiopathic factors can cause Uveitis.
Infections may include viruses or bacteria, while autoimmune conditions lead to the immune system attacking the eye.
Trauma and idiopathic cases also contribute to Uveitis onset.
How long does it take for Uveitis to clear up?
The duration for Uveitis to clear up varies.
It can last from weeks to months, depending on the type of treatment, severity, and individual reaction.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management contribute to a more favorable prognosis.
How long does blurred vision last with Uveitis?
The duration of blurred vision caused by Uveitis varies depending on the type and severity of the condition.
While some people only have it for a few days or weeks, others with chronic or untreated Uveitis can have it for months and even result in blindness.
What does Uveitis pain feel like?
Uveitis pain is often described as a dull ache or discomfort.
Affected individuals may experience sensitivity to light, redness, and a feeling of pressure within the eye.
Consultation with an eye care professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management.
What is the difference between Uveitis and Iritis?
Uveitis is a broader term encompassing inflammation of the uvea, while Iritis specifically refers to inflammation of the iris.
Iritis is a subtype of anterior Uveitis, indicating inflammation confined to the iris, while Uveitis involves inflammation affecting the entire uvea.
What is the difference between Uveitis and Iritis?
Uveitis is a broader term encompassing inflammation of the uvea, while Iritis specifically refers to inflammation of the iris.
Iritis is a subtype of anterior Uveitis, indicating inflammation confined to the iris, while Uveitis involves inflammation affecting the entire uvea.
When referencing outside resources, GoodRxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.