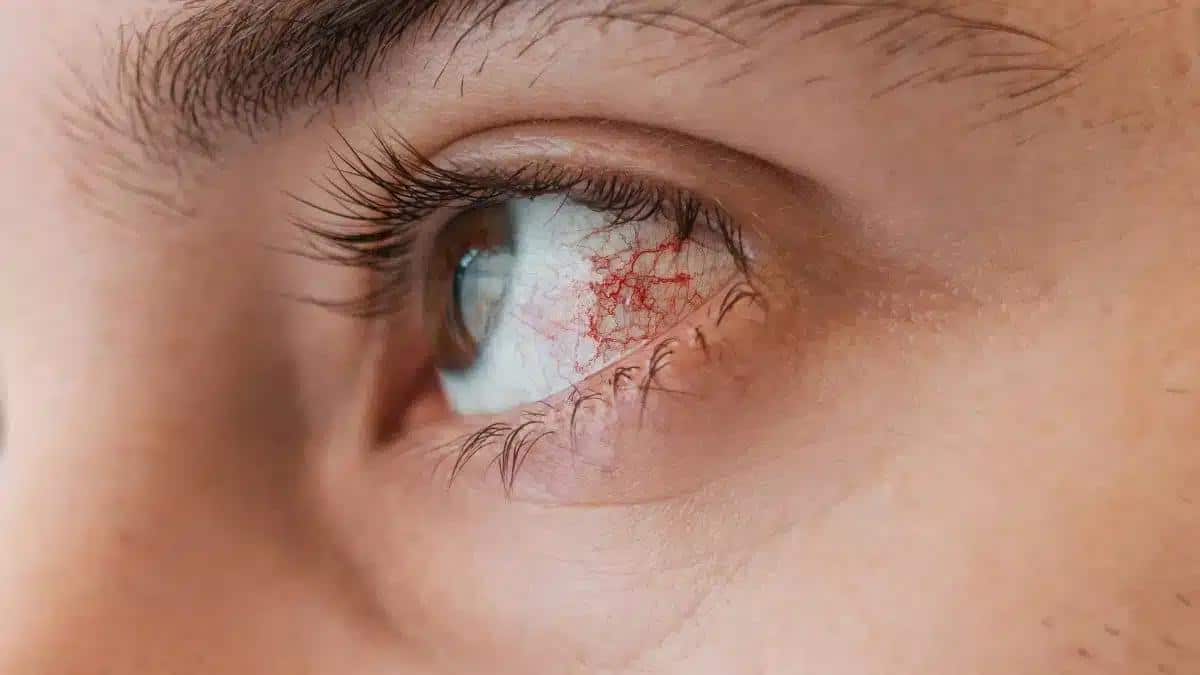
Posterior Uveitis, commonly known as Choroiditis, is the inflammation of the choroid.
The choroid is the back portion of the uvea, which can get inflamed due to microorganisms, toxins, and damaged tissue.
Posterior Uveitis can damage the optic nerve and retina.
This, in turn, may cause permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Read further to discover more about Posterior Uveitis.
Learn about its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Posterior Uveitis
Posterior Uveitis is the least prevalent type of Uveitis often linked to vision loss.
It is characterized by the inflammation of the choroid but may affect the retina and vitreous as well.
If untreated, Posterior Uveitis can lead to vision loss and other problems.
When the uvea becomes inflamed, cells accumulate in the choroid and the retina or float in the vitreous humor.
These cells may result in floaters or blurred vision.
Compared to other forms of Uveitis, Posterior Uveitis progresses far more slowly and can persist for several years.
Posterior Uveitis symptoms
 Source: zoranm_from_Getty_Images
Source: zoranm_from_Getty_ImagesUsually affecting just one eye, Posterior Uveitis shows its symptoms extremely slowly.
While some people do not experience any symptoms, those who do may find that they start suddenly and worsen rapidly.
Generally, Posterior Uveitis is painless and can lead to blurred vision.
The patient could have floaters, develop scotoma, and experience redness in the eyes.
Apart from this, people suffering from Posterior Uveitis may experience:
- Diminished visual acuity, or the sharpness of vision
- Light sensitivity
- Trouble seeing in the dark
- Difficulty recognizing color
A scotoma is a confined region of reduced vision in the visual field.
Don’t get confused between Uveitis and Iritis. Read our article: Iritis vs. Uveitis: Understanding the Key Differences to know the differences between the two.
Posterior Uveitis causes
Posterior Uveitis has several causes, but in many cases, the underlying cause may remain unknown.
A person’s immune system, infections, tumors, bruises, eye injuries, or exposure to toxins can all lead to Posterior Uveitis.
Both infectious and noninfectious factors can induce Posterior Uveitis.
Based on its causes, Posterior Uveitis can be classified as infectious and noninfectious Posterior Uveitis.
Infectious Posterior Uveitis is caused by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections.
These comprise cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, and Candidiasis.
Whereas noninfectious Posterior Uveitis can be brought on by autoimmune conditions.
These include Sarcoidosis, Wegener granulomatosis, Lupus erythematosus, and White dot syndrome.
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis is commonly linked to the disease in children.
Individuals with weakened immune system conditions, like individuals with HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to infectious Posterior Uveitis.
Also, if you are a cigarette smoker, then it becomes quite hard to manage the condition.
Diagnosing Posterior Uveitis
An eye exam is done to examine vitreous humor using the direct observation of inflammation and white blood cells.
Your doctor may inquire about your medical history and may suggest some further laboratory testing.
This is done to determine if immunological or infectious problems are the source of the symptoms.
Blood tests can be performed to check for infections caused by spirochetes, toxoplasmosis, herpes virus, and toxocariasis.
Chest X-rays can also be done to identify the presence of tuberculosis or sarcoidosis.
Posterior Uveitis treatment
Posterior Uveitis can cause scars on the interior of the eye and may result in other conditions that can impair vision.
Hence, it has to be addressed as soon as possible.
The root cause and severity of Posterior Uveitis usually determine the course of treatment.
Medications, such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, biologics, and surgery, are mostly employed to treat Posterior Uveitis.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are the most often prescribed medication to treat Posterior Uveitis.
These can reduce the degree of inflammation, redness, and itching.
The medication can be given in the form of oral pills, eye drops, or injections, depending on the parts of the eye that are affected.
Immunosuppressants
If the origin of the condition is an autoimmune disease, immunosuppressants are advised.
Immunosuppressants suppress inflammation and inhibit the immune system.
Biologics
Biologics are the recommended course of action if other commonly used immunosuppressants won’t work.
These are the therapeutic proteins designed to inhibit the actions of bioactive immune response mediators.
Surgery
 Source: Raul_Infante_Gaete_From_Pexels
Source: Raul_Infante_Gaete_From_PexelsIn rare instances, Posterior Uveitis surgery is carried out.
Surgery can be done if you frequently get Uveitis in your eyes.
The surgical procedure is intended to enhance visual clarity by replacing the aqueous humor, or fluid, inside the eye.
Conclusion
Posterior Uveitis, the inflammation of the choroid, is a rare form of Uveitis.
Its symptoms manifest slowly and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
Posterior Uveitis occurs due to a person’s immune system, infections, tumors, bruises, eye injuries, or exposure to toxins.
Early detection and treatment are required for reducing the chances of any complications associated with the condition.
Your doctor may prescribe medications like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and surgery based on the severity and cause of Posterior Uveitis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of Posterior Uveitis?
Posterior Uveitis could be the result of infections, tumors, bruises, eye injuries, or exposure to toxins.
What is the best treatment for Posterior Uveitis?
Oral corticosteroids are the most effective first line of treatment for Posterior Uveitis.
In severe conditions, corticosteroids can be given in the form of injection.
Infections leading to Posterior Uveitis may be overcome with antivirals, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications.
How is Posterior Uveitis diagnosed?
Posterior Uveitis can be diagnosed by a thorough eye examination and evaluation of the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
Can Posterior Uveitis cause vision loss?
Yes, Posterior Uveitis can affect the optic nerve and retina leading to vision loss.
How can you distinguish between Anterior Uveitis and Posterior Uveitis?
The iris in the front of the eye is affected by Anterior Uveitis.
Whereas the retina and choroid in the back of the eye are impacted by Posterior Uveitis.
When referencing outside resources, GoodrxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.