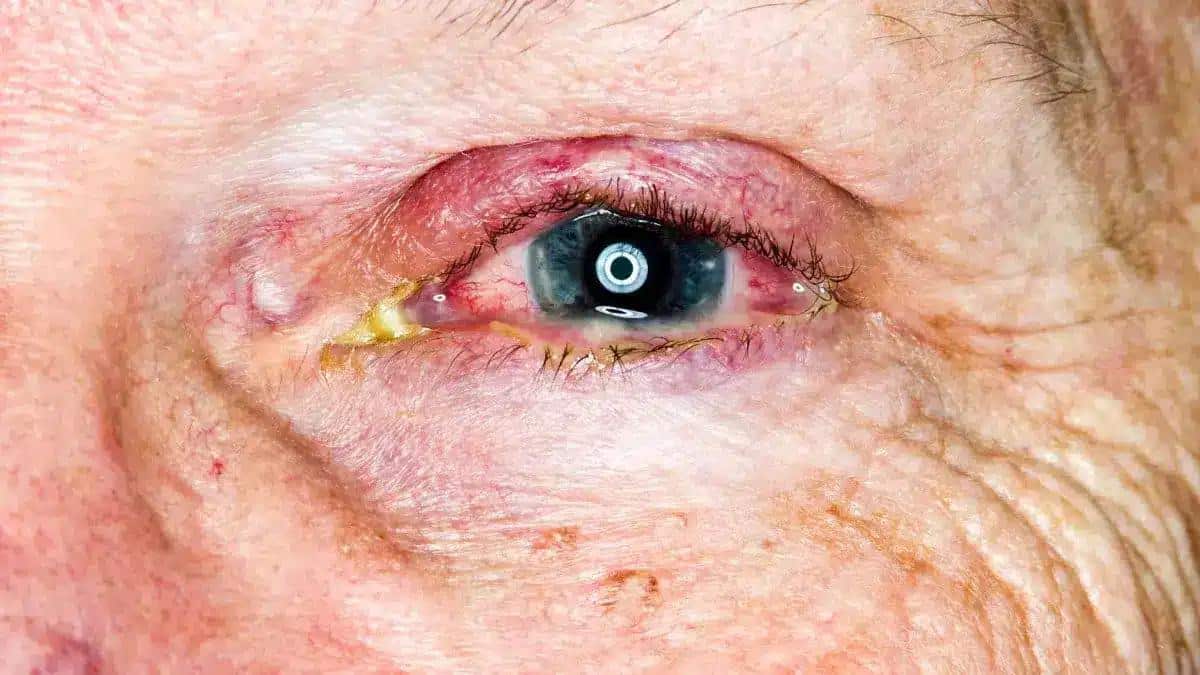
Keratitis is characterized by corneal inflammation, which causes eye pain and discomfort.
Filamentary Keratitis is frequently caused by ocular surface abnormalities or eye injury.
If Filamentary Keratitis is left untreated, it might lead to permanent vision loss.
However, this condition can be avoided with early detection and treatment.
This article discusses Filamentary Keratitis, its symptoms, causes and treatment available.
What is Filamentary Keratitis
Filamentary Keratitis is linked to several ocular conditions, the most common of which is Dry Eyes.
It is characterized by the existence of thread-like structures on the surface of the cornea.
Infected individuals may experience a sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
Filamentary Keratitis is an uncommon condition that has the potential to cause vision loss.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment is essential to avoid potential risks and side effects.
Filamentary Keratitis symptoms
 Source: zoranm_from_Getty_Images
Source: zoranm_from_Getty_ImagesFilamentary Keratitis has various symptoms that can significantly affect eye health.
It is a noninfectious kind of Keratitis that varies from person to person.
It is essential to recognize symptoms of Filamentary Keratitis for prompt medical attention.
Some symptoms of Filamentary Keratitis are:
Blurry vision: Filaments may cloud eyesight, resulting in blurry or hazy vision.
Eye discomfort: Individuals frequently report feeling something in their eye, causing irritation and discomfort.
Increased tear production: Excessive tearing may occur as the eye attempts to reduce inflammation.
Redness: The eye may become red and swollen due to the discomfort created by the filaments.
Light sensitivity: Patients may become more light-sensitive, resulting in photophobia.
Regular monitoring is required to ensure good eye health and to reduce the impact of this complicated and painful condition.
To learn more about Keratitis symptoms in detail, Read Keratitis Symptoms: Understanding the Signs of Corneal Inflammation
Causes of Filamentary Keratitis
 Source: Pixeloit
Source: PixeloitVarious factors, such as ocular surface abnormalities and eye injuries, can cause Filamentary Keratitis.
It can also result from extended use of contact lenses or underlying medical conditions.
Let’s discuss some of the causes of Filamentary Keratitis:
Dry Eyes: It is one of the most common causes of Filamentary Keratitis. When your eyes do not generate enough tears or when the tears evaporate too soon, this can cause corneal damage and filament formation.
Contact lenses: Contact lens misuse or extended use may result in the development of Filamentary Keratitis.
Underlying medical condition: Filamentary Keratitis can be aggravated by conditions such as Sjögren’s Syndrome, Ocular Rosacea, and viruses such as herpes simplex.
Corneal damage: Filamentary Keratitis can also be caused by corneal trauma or injury, such as scrapes or burns.
Understanding these causes is essential for treatment and preventing recurrence of the condition.
Want to learn more about treatments available for Dry Eyes, Read Effective Dry Eye Treatment: Relieve Irritation and Improve Eye Health
Ocular Rosacea is a condition involving eye irritation and inflammation linked to facial rosacea.
Filamentary Keratitis treatment
Treatments for Filamentary Keratitis are essential to relieve symptoms and underlying causes.
Filamentary keratitis is a complex eye condition that requires prompt medical assistance to avoid side effects.
Lubricating eye drops can aid in the relief of dryness and irritation.
Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory or antibiotic eye drops to minimize inflammation and manage any infection.
When the filaments break off, leaving epithelial flaws behind, your eye doctor may propose bandage contact lenses in extreme situations.
Follow proper hygiene to avoid Filamentary Keratitis caused by extended use of contact lenses.
Regular check-ups are essential to track progress and fine-tune treatments for the best results in managing Filamentary Keratitis.
Summing up
Filamentary Keratitis is a noninfectious Keratitis that is characterized by the production of filaments on the corneal surface.
Some of the symptoms of Filamentary Keratitis are blurry vision, eye discomfort, redness, and more.
Filamentary Keratitis is caused by underlying medical conditions such as Ocular Rosacea.
Corneal damage and Dry Eyes can also lead to Filamentary Keratitis in some individuals.
Some treatments available for Filamentary Keratitis are lubricating eye drops and contact lens care.
It is essential to consult an eye care professional for proper diagnosis and effective management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Filamentary Keratitis serious?
Filamentary Keratitis can be serious as it may cause significant discomfort, impact vision, and lead to complications.
Seeking timely medical attention for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment is crucial for managing this ocular condition effectively.
How to remove filament Filamentary Keratitis?
The removal of Filamentary Keratitis involves professional care.
An eye care professional may gently remove the filaments using specialized instruments during an examination.
Attempting self-removal may worsen the condition and is strongly discouraged.
Can Filamentary Keratitis be prevented?
No, Filamentary Keratitis cannot always be prevented. However, practicing proper eye hygiene and controlling underlying medical conditions can lower your risk.
What home remedies are available for Filamentary Keratitis?
Home remedies such as warm compresses and artificial tears can help manage discomfort.
However, a proper diagnosis and treatment plan requires the consultation of a healthcare professional.
What causes Filamentary Keratitis?
Filamentary Keratitis is often caused by conditions leading to irregular tear composition, ocular surface abnormalities, or eye injuries.
Other factors include dry eyes, inflammation, and improper contact lens use.
When referencing outside resources, GoodrxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.