Interstitial Keratitis is an eye condition that involves the inflammation of the deeper layers of the cornea (the clear, outermost layer of the eye).
This condition stems from various factors, including infections and noninfectious triggers. Symptoms can vary based on the causes and type of Interstitial Keratitis.
A thorough diagnosis is required to determine the underlying cause for specialized care.
This article delves into Interstitial Keratitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential effects on eye health.
What is Interstitial Keratitis
Interstitial Keratitis or Ocular Interstitial Keratitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the cornea’s deeper layers.
This type of Keratitis is characterized by the inflammation of the middle layer of the cornea or the stroma.
It occurs when the blood vessels grow into the cornea, decreasing corneal transparency. It can also cause eye pain, blurry vision, pPhotophobia (sensitivity to light), and redness.
Based on its severity and the affected part of the eye, Interstitial Keratitis may be Necrotizing or Bilateral.
Necrotizing Interstitial Keratitis is a severe form of the condition, which causes rapid corneal tissue damage.
Bilateral Interstitial Keratitis is another form of the condition that affects both eyes simultaneously.
Buy now: Eye Care
Causes of Interstitial Keratitis
Interstitial Keratitis can develop from infectious or noninfectious factors. It can be categorized into various types based on the causes, severity, and impact on vision.
Let us discuss what causes Interstitial Keratitis. The following infectious agents can trigger the development of this condition:
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): An HSV infection can cause Interstitial Keratitis, leading to inflammation in the corneal layers.
Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): You can also get Interstitial Keratitis from Varicella Zoster. This viral infection contributes to corneal inflammation.
Syphilis: Secondary Syphilis, which develops from Treponema pallidum infection, is the most common cause of Interstitial Keratitis, known as Syphilitic Interstitial Keratitis.
In some cases, Interstitial Keratitis can also develop from other fungal or bacterial infections.
In addition, this condition can also arise from noninfectious causes, including:
- Autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis or Lupus
- Eye trauma or injury from scratches or chemical exposure
- Genetic factors
- Lyme disease
Symptoms of Interstitial Keratitis
 Source: dtimiraos_from_Getty_Images
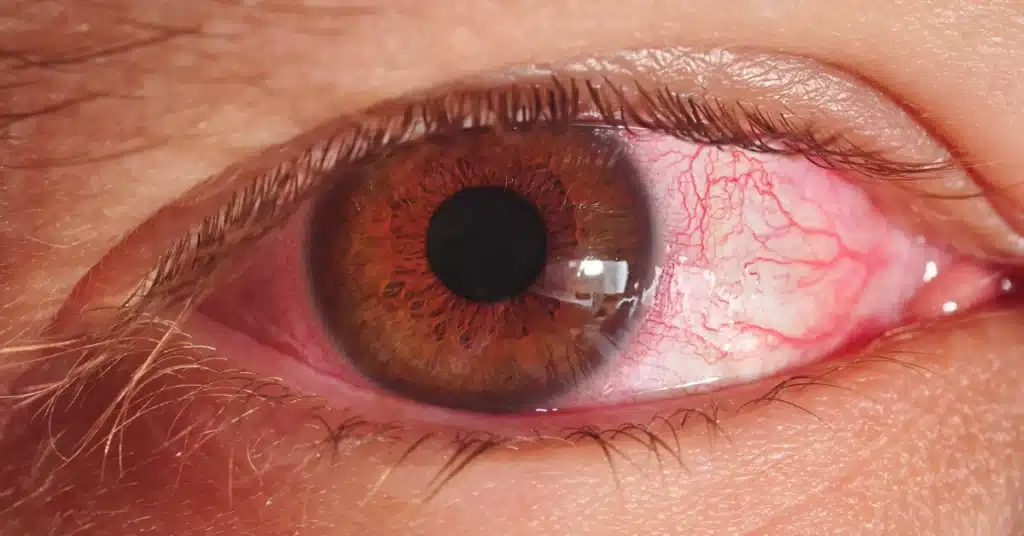
Source: dtimiraos_from_Getty_ImagesInterstitial Keratitis presents various symptoms, such as redness in the eye, blurry vision, eye pain and sensitivity to light.
However, you may wonder, “What does Interstitial Keratitis look like?” The following questions visual indicators can help recognize the symptoms of this form of Keratitis:
Corneal haze: The affected cornea may appear cloudy, hazy, or less transparent.
Grayish opacity: Grayish or whitish opacity within the cornea may be apparent.
Redness: The white part of the eye may appear red due to inflammation in the affected area.
Corneal Infiltrates: Inflammatory cells and deposits may be detected within the corneal layers.
Duration and progression of Interstitial Keratitis
The duration and progression of Interstitial Keratitis can vary greatly depending on the underlying cause, treatment approaches, and individual factors.
Let us learn how long Interstitial Keratitis lasts and how it progresses, especially if left untreated.
How long does Interstitial Keratitis last
Interstitial Keratitis can last for weeks to months without treatment. In some cases, it can become chronic, causing long-term corneal damage.
However, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly minimize the duration of symptoms.
After starting treatment, individuals may notice improvement in their symptoms within a few weeks.
How does it progress
In its early stages, Interstitial Keratitis can cause symptoms such as red eyes, discomfort, light sensitivity, and blurred vision.
The untreated inflammation can lead to corneal scarring, increased opacity, and potential vision impairment or blindness.
Necrotizing forms of Interstitial Keratitis can cause rapid and severe tissue damage if not addressed immediately. It can lead to substantial vision impairment.
Diagnosis and treatment
 Source: Industrial_Photograph
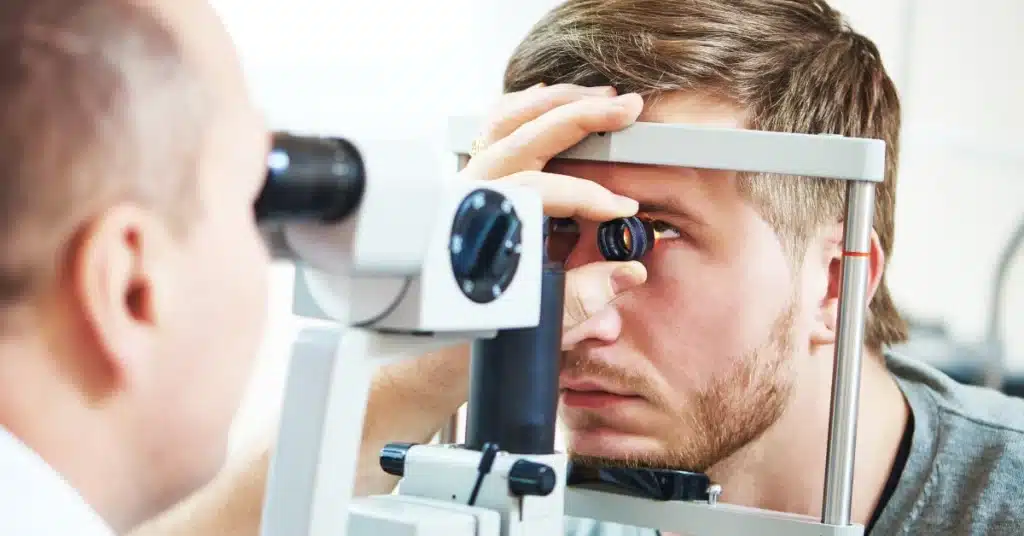
Source: Industrial_PhotographIt is essential to seek immediate medical attention from an eye care professional to diagnose and treat Interstitial Keratitis properly.
The treatment approaches depend on the underlying cause, severity, and the patient’s overall health condition.
How is Interstitial Keratitis diagnosed
An eye care professional will conduct a slit-lamp examination of the eyes to diagnose Interstitial Keratitis.
The slip lamp helps assess the structure of the cornea for haze, inflammation, or opacity.
Blood tests and chest X-rays are typically necessary to confirm the infection or disease underlying the condition.
How do you treat Interstitial Keratitis
Treatment for Interstitial Keratitis involves targeting the underlying cause. Antiviral or antibiotic medicines can help treat infectious causes.
Certain anti-inflammatory medicines, such as corticosteroids, can help reduce corneal inflammation and relieve symptoms.
Keratitis eye drops, or medications help manage discomfort or pain associated with this condition.
Eye protection with patches or shields may be required for comfort and safety.
Follow-up appointments are critical for monitoring progress and adjusting treatment as needed.
Summing up
Interstitial Keratitis is a condition that causes inflammation in the stroma, the middle layer of the eye’s cornea.
Infections, such as Syphilis, HSV, and VZV, often cause it. However, noninfectious factors, such as autoimmune conditions, eye trauma, and genetic factors, may also be responsible.
It leads to reduced transparency of the cornea, resulting in cloudiness or haziness. It also causes redness, eye pain, and blurry vision.
The condition necessitates immediate treatment and specialist care. It is important to recognize symptoms and seek prompt medical attention.
Early action can reduce discomfort, prevent visual issues, and protect eye health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ocular Interstitial Keratitis?
Ocular Interstitial Keratitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the deeper corneal layers (stroma), leading to haziness or opacity in the eye’s front surface.
What are Interstitial and Deep Keratitis?
Interstitial Keratitis is a corneal inflammation affecting the cornea’s middle layer, while Deep Keratitis affects the deeper layers.
Can Interstitial Keratitis cause blindness?
If untreated, cases of Interstitial Keratitis can lead to vision impairment or blindness due to corneal scarring.
Is Interstitial Keratitis seen in Secondary Syphilis?
Yes, Interstitial Keratitis is a common eye manifestation of secondary syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum infection.
Is Interstitial Keratitis painful?
Interstitial Keratitis may cause eye pain or discomfort due to corneal inflammation.
Is Interstitial Keratitis infectious?
Interstitial Keratitis can be infectious, often caused by viral, bacterial, or fungal agents affecting the cornea’s deeper layers.
When referencing outside resources, GoodrxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.