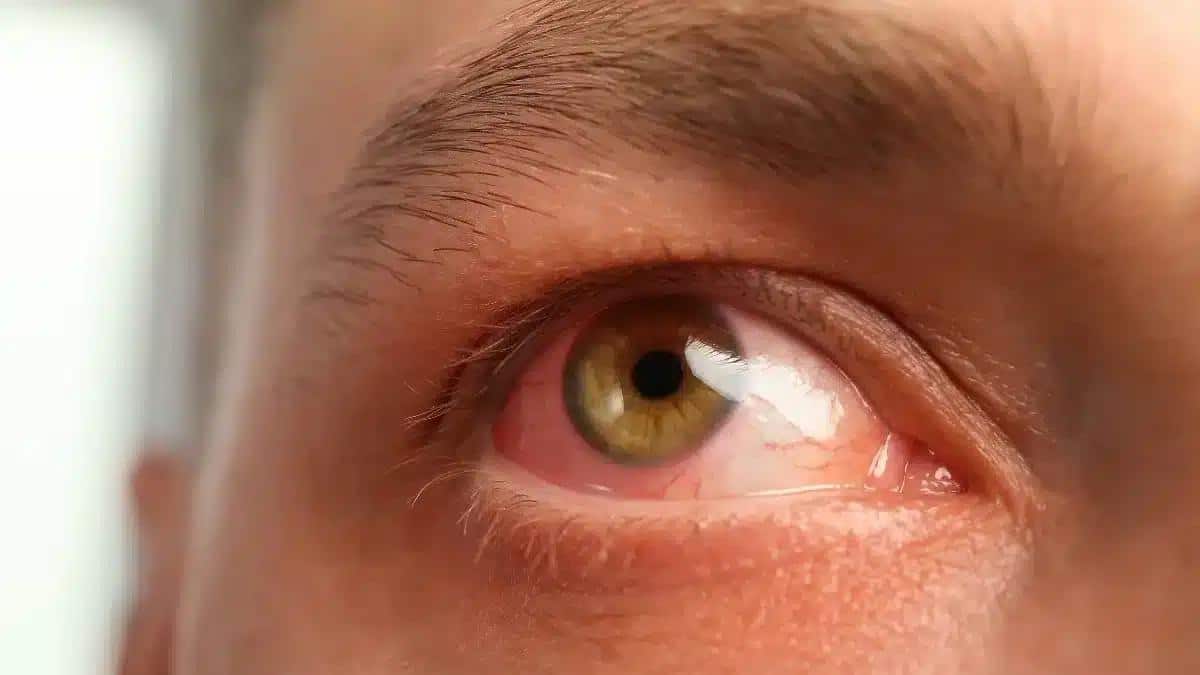
Eye infection is a common condition that may cause inflammation, redness, itching, discharge, and more.
Finding the right treatment is important for quick recovery and preventing complications.
However, the proper treatment depends on the type and cause of the eye infection.
Antibiotics are often prescribed to help treat some eye infections caused by bacteria.
Let us explore more about antibiotics for eye infections, their types, effectiveness, and side effects.
When are antibiotics used for eye infection
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial eye infections such as Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis), Bacterial Keratitis, and other infections.
The common eye infection symptoms include eye redness, swelling, discharge, and blurred vision.
The antibiotic medicines help ease the symptoms by stopping the growth and spread of the bacteria responsible for the infection.
However, antibiotics are not effective against fungal or viral eye infections.
Consult an eye doctor for proper diagnosis and effective eye infection treatment.
Types of antibiotics for eye infection
The antibiotic prescribed for eye infection depends on the type and severity of the infection.
The two types of antibiotics commonly used for treating eye infections are topical and oral.
Let us explore the types of antibiotics in detail.
Topical antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are medications specifically for external use on the eyes.
They come in the form of eye drops or ointments and are applied directly to the affected eye.
These antibiotics help treat infections by blocking the growth and spread of bacteria.
Common examples of topical antibiotics include Neomycin, Polymyxin B, and Bacitracin.
Eye drops are popular for mild bacterial infections, as they provide targeted treatment and are easy to use.
On the other hand, ointments offer a longer-lasting effect and are often preferred for nighttime applications.
Oral antibiotics
 Source: Signature_images
Source: Signature_imagesOral antibiotics are medications taken by mouth that circulate through the bloodstream to reach the infected area.
These antibiotics are prescribed for more severe eye infections or infections that have spread beyond the eye.
A study states that oral antibiotics like Azithromycin or Doxycycline are effective in treating Chlamydial Conjunctivitis.
Oral antibiotics are prescribed when the infection is not limited to the surface of the eye.
Consult a doctor for proper antibiotic treatment options.
Over-the-counter antibiotics for eye infection
The over-the-counter (OTC) antibiotic options for bacterial eye infections are limited.
The OTC medications help treat external bacterial infections by blocking bacterial growth.
However, one should avoid OTC antibiotic medicines as they have limited scientific studies.
Moreover, self-diagnosis can lead to ineffective use of medicine or unwanted side effects.
Always consult a doctor for proper eye diagnosis and appropriate eye infection medicine.
Side effects of antibiotics for eye infection
 Source: instaphotos
Source: instaphotosAntibiotics for eye infections are generally safe and effective, but they may sometimes cause side effects.
Common side effects of topical antibiotics include temporary stinging or burning upon application.
Some individuals may also experience mild irritation, itching, or redness. However, these side effects are mild and temporary.
On the other hand, oral antibiotics are prescribed for more serious eye infections and may cause issues like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Consult your eye doctor for other eye infection medicine if you experience the above side effects constantly.
Key takeaways
Antibiotic medicines are a good treatment option for eye infections. However, the treatment depends on the cause of the eye infection.
The medicine only fights against bacterial eye infections, not viral or fungal ones.
The two types of antibiotics commonly used for treating eye infections are topical and oral.
Antibiotic medications help target and eliminate bacteria and ease the symptoms of eye infections like redness, itching, and more.
Consult a doctor for proper antibiotics for eye infection, complete the full treatment, and be aware of potential side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for antibiotics to clear up bad eye infections?
Antibiotic medicine may take 24 to 48 hours to work and show effectiveness. However, the duration of antibiotic treatment may vary for everyone and depends on factors like the severity of the infection and the type of antibiotics prescribed.
What to do if eye infections are not responding to antibiotics?
Consult an eye doctor if the eye infections do not respond to antibiotics. The doctor may change the medicine dosage or prescribe a different antibiotic. The doctor may also perform an eye test to ensure the infection’s cause is bacterial.
Can an eye infection return after antibiotics?
Yes, an eye infection can return after antibiotics if the full course of treatment is not completed. Incomplete treatment may not eliminate the bacteria and lead to the recurrence of the infection. Consult an eye doctor if the eye infection symptoms are consistent.
What is the best antibiotic for eye infections in adults?
The choice of the best antibiotic for eye infections in adults depends on the specific type of infection. The commonly prescribed antibiotics include Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, and more. However, the appropriate antibiotic is decided based on the doctor’s diagnosis.
Can I use expired antibiotics for eye infections?
No, one should not use expired antibiotics for eye infections. Expired medications are less effective and may cause unwanted side effects. Consult a doctor for a new prescription for eye safety and treatment efficacy.
When referencing outside resources, GoodrxMedicine always provides full citations. To learn more about the measures we use to maintain the quality of our content, please review our Content Information Policy.